This section provides guidance on Vehicle Tracking and Dust Control, Section 3 in the Construction BMP Handbook.
A PDF of this entire section can be downloaded here.
Click on the topics below to navigate to the each section.
DESCRIPTION
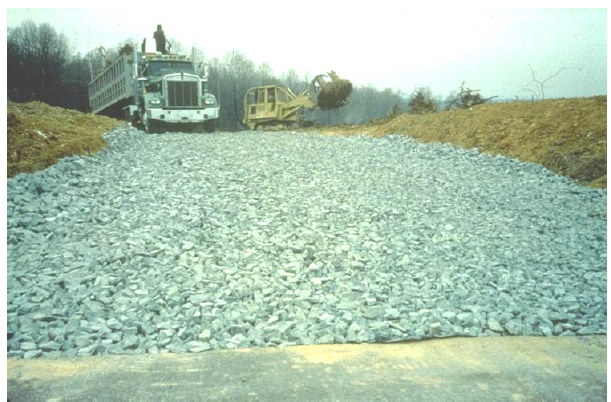
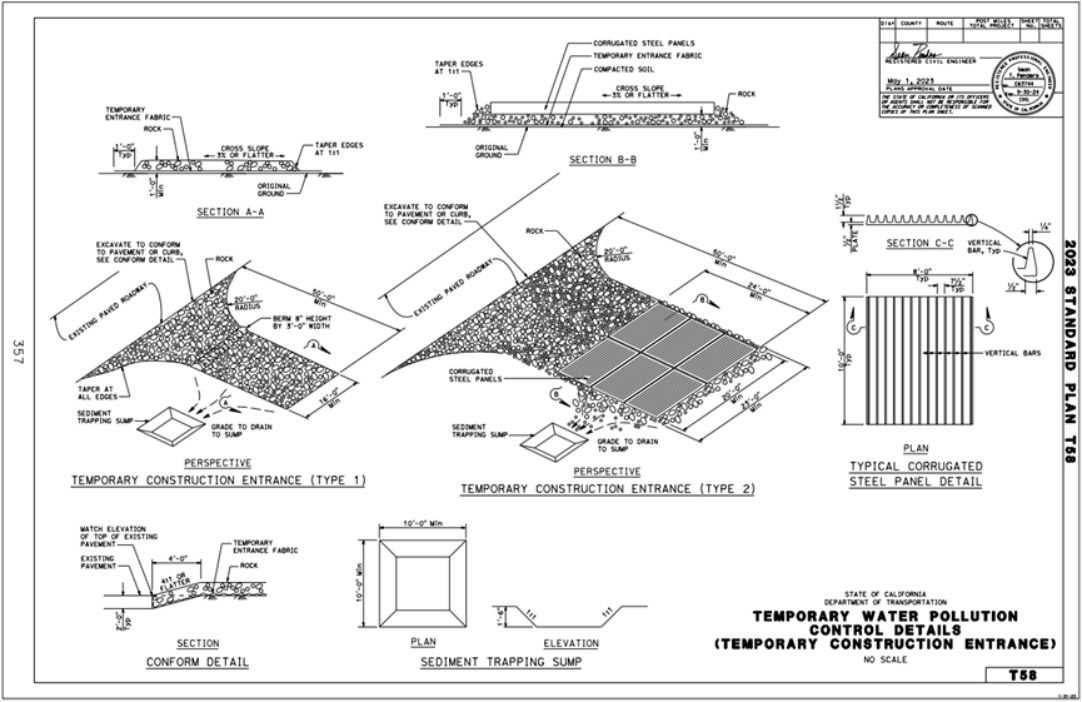
Stabilized construction access is required to minimize the tracking of soils and sediment from vehicles leaving the construction site. A rock pad or a construction mud mat at the site’s exit/entrance should be installed to protect streets and public rights-of-ways. Construction mud mats are less time- and labor-intensive and may be better suited for smaller, more urban sites due to space constraints.
GUIDELINES
- Install the construction entrance after fencing off “no disturbance” areas and establishing perimeter controls.
- Design mats and rock pads to support the heaviest and widest equipment entering the project site.
- Anchor construction mud mats to the adjacent surface to ensure stable placement.
- Grade the construction exit/entrance to prevent runoff from leaving the site.
- Direct all runoff from the access through a sediment-trapping device prior to discharge.
MAINTENANCE
Inspect the construction access points daily. If clogged with sediment and debris, clean or replace the rock or mats. Maintenance also includes the cleaning and repair of any structures used to trap sediment.
All materials spilled, dropped, washed, or tracked from vehicles onto roadways or into the stormwater collection system shall be removed or cleaned up immediately, by no later than the end of the work day. Applying water to the roadway before sweeping or vacuuming may help loosen sediment, provided that discharge to the stormwater collection system does not occur.
DESCRIPTION
Efficient construction road stabilization reduces onsite erosion. It can help to avoid instances of immobilized machinery and delivery vehicles, improving site efficiency and working conditions overall during adverse weather.
Stabilization of construction roads should occur under the following conditions:
- During wet weather
- During activities that create dust
- When adjacent to water bodies
- When soils are easily erodible
- Where phased construction will cause roads to be placed in and out of service
GUIDELINES
- Access roads, driveways, subdivision roads, parking areas, and other on-site vehicle transportation routes should be stabilized immediately after grading.
- A temporary gravel roadway should be considered during the rainy season and on slopes greater than five percent.
- Roadway slope should not exceed fifteen percent without an alternate surface material. Design stabilized access to support heavy vehicle and equipment use.
- The temporary roadway must be removed, restored, and permanently stabilized when construction is complete.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
Periodically, apply additional aggregate or base material on gravel roads. If using a soil based construction road, apply water at a minimum of three times per day during the dry season for dust control, or as indicated from site traffic. Increase water application according to site traffic.
Properly installed stabilized roadway
No stabilized roadway
DESCRIPTION
Tire wash facilities should be located at construction access points. They remove sediment from tires and undercarriages and prevent sediment from being transported onto roadways. The wash water should be discharged to a settling basin or dewatering device prior to leaving the site.
GUIDELINES
- Incorporate tire wash facilities with a stabilized construction access. There should be a separate drive-out space for the tire wash.
- Construct tire wash facilities on level ground when possible, or on a pad of coarse aggregate. A geotextile fabric should be placed below the aggregate.
- Wash racks should be designed and constructed to support anticipated traffic loads.
- Use a drainage ditch to convey the runoff from the wash area to a sediment trapping device. The drainage ditch should be of sufficient grade, width, and depth to carry the runoff.
- Direct all traffic leaving the site with mud-caked tires and/or undercarriages use the wash facility.
- Barricades may be installed to collect, control, and hold wash water, especially over asphalt and concrete surfaces.
MAINTENANCE AND INSPECTION
Inspect the tire wash area daily. Remove trapped sediment on vehicles to ensure it does not travel offsite and enter the storm drain system.
SIGNS OF FAILURE = mud stays on tires
tire wash facility installed

No tire wash used
DESCRIPTION
Street sweeping and vacuuming must be used where soil is tracked from the project site, to prevent sediment from entering storm drains and receiving waters. They may be used to remove tracked soils, sand, and other debris from public streets and paved areas.
GUIDELINES
- Streets should be cleaned with a broom or mechanical methods, such as vacuuming.
- The site manager is responsible for cleaning construction vehicles leaving the site on a daily basis.
- Adjacent street frontages should be swept at least once a day to remove silt and other construction related debris.
- Dispose of sweeper wastes at an approved dump-site.
types of approved mechanical street sweepers
- Mechanical sweeper followed by a vacuum-assisted sweeper
- Vacuum-assisted, dry, waterless, sweeper
- Regenerative-air sweeper
Violations of street sweeping requirements
proper street sweeping operations

DESCRIPTION
Dust control reduces surface activities and air movement that cause dust to be generated from disturbed soil areas. These practices consist of applying water or commercial stabilizers to prevent or minimize generation of dust.
GUIDELINES - Structural Controls
The following examples are methods of dust control to be used during work site operations:
- Stabilize storage, vehicle movement, and parking areas by installing gravel over geotextile fabric.
- Install or maintain vegetative or structural barriers.
- Sweep or vacuum paved surfaces to remove tracked soil.
- Apply mulch to exposed soil.
- Use tarps to cover stockpiles.
- Load trucks carrying excavated material so that the material does not extend above the walls or back of the truck bed. Wet the surface of each load and tightly cover before the haul truck leaves the loading area.
WATER SPRAYING
Mist the immediate excavation area with a water spray to prevent airborne dust particles. During dust generation activities, perform continuous water spraying.
While spraying, be sure to prevent ponding and/or generation of runoff that could potentially reach storm drain inlets.
COMMERCIAL STABILIZERS
Chemical based stabilizers may be used on site as an alternative to water. Stabilizers include tackifier mixtures and other binding agents. Stabilizers typically come in a concentrated form and are applied through a surface spray either by a water truck or a handheld sprayer.
dust control in action